Summary of Components
So far, all of our interaction with Cardano has been through the cardano-cli and a locally running cardano-node. While it is perfectly fine for one-off tasks and goals, building complex products/protocols entirely in a scripting languages will prove difficult to maintain and scale. Further, most developers are far more productive building in their preferred languages and ecosystems.
A Birds Eye View
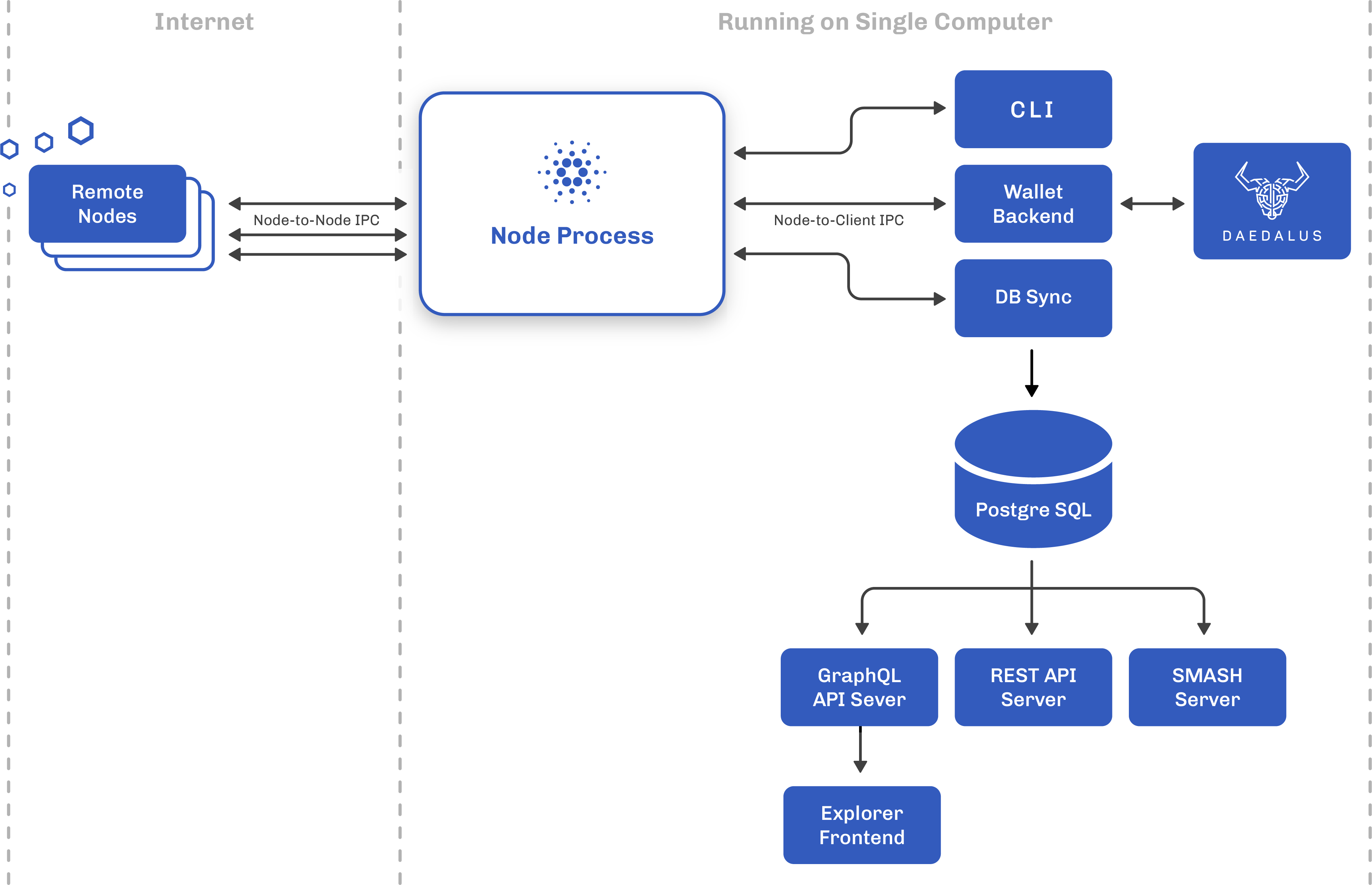 Image courtesy of Cardano docs
Image courtesy of Cardano docs
🚧 Thorough Overview Diagram coming soon
As described in our earlier post Running a Full Cardano Node, through a set of bespoke protocols the cardano-node serves as the main integration point to many downstream components utilising the node-to-client protocol. These downstream components can:
- Perform ad-hoc queries through the
local-state-querymini-protocol - Submit transactions via the
local-tx-submissionmini-protocol - Propagate, consume and persist chainDB data through the
chain-syncmini-protocol
Over the course of our Getting Started content, our guides made use of the first two mini-protocols using the cardano-cli to query the chain and submit our transactions. We will touch on the third chain-sync protocol in our following post on querying the chain.
For many developers the biggest hurdle with integration stems from the fact that these cardano-node specific protocols are not meant for external public consumption, and even direct internal consumption can be difficult if you are not familiar with Haskell. Luckily there are two options - you can either host your own pipeline of components to integrate with Cardano or rely on community-built SDKs and external hosted APIs.
Self-hosted vs External APIs
🚧 More content coming soon
Use-cases
ECommerce
- A store creates and manages sets of keys to generate payment addresses to receive payments for orders
- A customer creates and manages their own set of keys and addresses through their wallet(s)
- The store listens for customer payments at their payment addresses
- The customer submits a transaction as a payment to the store’s given address with additional metadata of purchase
- For every valid payment the store will create and process an order in their (off-chain) systems
- The store either
- Records a successful order on-chain via a new transaction with metadata
- Refunds the payment back to the customer if it cannot be fulfilled
🚧 More content coming soon
Advanced Queries for Cardano
Continue to Querying the Chain ➡️


