NFT Minting Guide
Using a similar approach as our Fungible Token Minting Guide , we can mint Cardano NFTs (aka CNFTs) with four basic steps:
- Create Token Minting Policy
- Create Wallet Keys and Addresses
- Upload Image to IPFS
- Build and Submit Minting Tx with Metadata
📝 The main differences involve creating a stricter minting policy, uploading our image to IPFS, and attaching NFT-specific metadata
Goals
After following this guide you will learn how to make your own token minting policy and mint a single NFT after uploading your image to IPFS.
Prerequisites
From our previous post Running a Full Cardano Node
- The
cardano-clibinary - The
cardano-nodebinary that is actively running and fully synchronised
Create Token Minting Policy
Create Policy Key
A policy key can be generated using the same approach as generating a payment address key as described in our page Getting Started - Wallet Basics: Keys and Addresses.
cardano-cli address key-gen \
--verification-key-file nft-policy.vkey \
--signing-key-file nft-policy.skey
Capture the hash of the key in the shell variable POLICYKEYHASH by running
POLICYKEYHASH=$(cardano-cli address key-hash --payment-verification-key-file nft-policy.vkey)
Define Multisig Policy
As mentioned earlier, NFTs must guarantee that only one token exists for a policyID and asset name combination. This can be defined in a Multisig policy with a time locking script to ensure tokens can only be minted before a certain time. This applies across the entire policy so in other words, that policyID cannot be used to mint any tokens after that time regardless of its asset name.
📝🕰️ Time is denoted in slots since the genesis and a slot is a second as configured for the current protocol configuration. See our explanation
Create a nft-policy.script file with the right script using
SLOTS_BEFORE_EXPIRY=3600
EXPIRES_AT_SLOT=$(expr $(cardano-cli query tip --testnet-magic 1097911063 | jq .slot) + $SLOTS_BEFORE_EXPIRY)
touch nft-policy.script
echo "{" >> nft-policy.script
echo " \"type\": \"all\"," >> nft-policy.script
echo " \"scripts\":" >> nft-policy.script
echo " [" >> nft-policy.script
echo " {" >> nft-policy.script
echo " \"type\": \"before\"," >> nft-policy.script
echo " \"slot\": $EXPIRES_AT_SLOT" >> nft-policy.script
echo " }," >> nft-policy.script
echo " {" >> nft-policy.script
echo " \"type\": \"sig\"," >> nft-policy.script
echo " \"keyHash\": \"$POLICYKEYHASH\"" >> nft-policy.script
echo " }" >> nft-policy.script
echo " ]" >> nft-policy.script
echo "}" >> nft-policy.script
📄 nft-policy.script
{
"type": "all",
"scripts":
[
{
"type": "before",
"slot": 54852747
},
{
"type": "sig",
"keyHash": "0f2a601505ecb9f008861c85293a34e2178ecd59c472619c5f895d9b"
}
]
}
This policy requires a signature from the nft-policy.skey key and specifies a time-locked validity of 3600 slots from the current tip of the chain. This is equivalent to 3600 seconds=60 minutes=1 hour from now based on the current slotLength: 1 protocol configuration.
📝❗ No more tokens can be minted after an hour so adjust to a higher number if you require longer to complete this guide.
You can then capture the policyId of the NFT’s multisig policy in the shell variable POLICYID by running:
POLICYID=$(cardano-cli transaction policyid --script-file nft-policy.script)
Create Wallet Keys and Addresses
We will then create another set of keys for two wallets. One source wallet to get testnet tADA from the faucet to cover the Tx fee, and one destination wallet to receive the minted tokens. Although in theory you can use the same policy key to generate an address to receive tADA and mint the custom tokens, we recommend using different sets of keys based on their purpose.
📝❗ In case of mainnet we will know the destination address upfront, so only one set of keys are needed. However as mentioned earlier, mainnet payment keys should be generated in a trusted air-gapped machine without any network connectivity
cardano-cli address key-gen \
--verification-key-file source.vkey \
--signing-key-file source.skey
cardano-cli address build \
--payment-verification-key-file source.vkey \
--out-file source.addr \
--testnet-magic 1097911063
cardano-cli address key-gen \
--verification-key-file dest.vkey \
--signing-key-file dest.skey
cardano-cli address build \
--payment-verification-key-file dest.vkey \
--out-file dest.addr \
--testnet-magic 1097911063
SOURCEADDR=$(< source.addr)
DESTADDR=$(< dest.addr)
📝 Note the final two lines where the addresses are captured in shell variables SOURCEADDR and DESTADDR
Load ADA from Testnet Faucet
Use the testnet faucet to send ADA to the generated source wallet address $SOURCEADDR.
You can then wait a short while and query that the tADA has reached your address by running:
cardano-cli query utxo \
--address $SOURCEADDR \
--testnet-magic 1097911063
Upload Image to IPFS
Blockchains are not designed nor optimised to store large file blobs so a separate decentralised file storage and content delivery solution is usually required for NFT content that exceed Cardano’s 16kB Tx metadata limit.
📝 NFTs can also be fully on-chain using various ingenious methods to ensure the content fits within the 16KB Tx metadata max payload. Examples of this are Stellar Hood, CardanoTrees, JurassikChained, Mandelbrots, Fractano, Aw0k3n and upcoming NFTs from Veritree
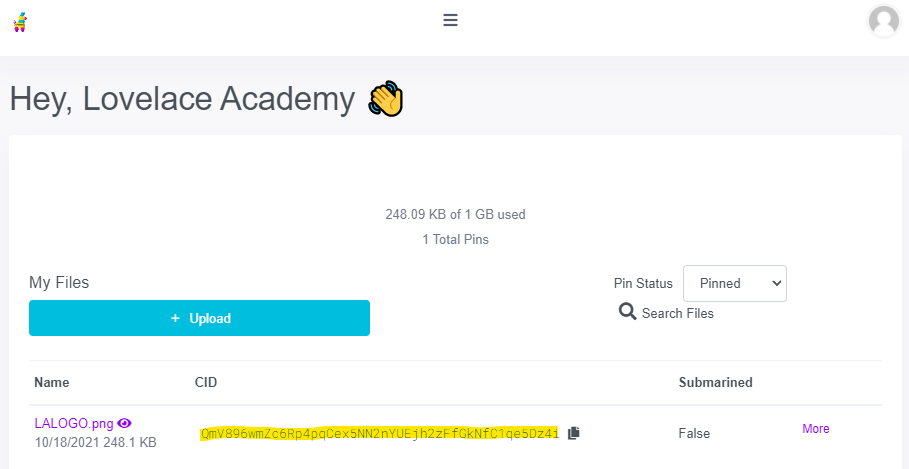
For content over 16KB, IPFS is the currently adopted solution for storing and serving content in the Web3 world. In order to quickly upload content pinned to IPFS without operating a full node, you can use a freemium service like Pinata and note the CID of your uploaded content. This CID will be used in the image field of your Tx metadata to point your CNFT to an IPFS URL. In this example we will use the Lovelace Academy logo as the image for our CNFT.
Minting Transaction
By querying the source address that received the 1000 tADA from the faucet, load the relevant UTxO details (hash, index and value) into shell variables.
UTXO0=$(cardano-cli query utxo --address $SOURCEADDR --testnet-magic 1097911063 | sed -n 3p)
UTXO0H=$(echo $UTXO0 | egrep -o '[a-z0-9]+' | sed -n 1p)
UTXO0I=$(echo $UTXO0 | egrep -o '[a-z0-9]+' | sed -n 2p)
UTXO0V=$(echo $UTXO0 | egrep -o '[a-z0-9]+' | sed -n 3p)
Build NFT Metadata
Cardano has an NFT Metadata standard which we will use to define the correct metadata for our CNFT so that wallets, explorers and other tools can interpret and display it correctly. We will create an nft-metadata.json file with the following content and replace $POLICYID with the correct policyID from the first step and $IPFS_CID with IPFS CID from the third step. Also note we are using text LALOGO as the asset name instead of the hexadecimal and to use the correct mediaType if you are using an image format other than image/png.
{
"721": {
"$POLICYID": {
"LALOGO": {
"name": "The Lovelace Academy Logo",
"description": "Our Logo for the Lovelace Academy NFT Minting Guide",
"mediaType": "image/png",
"https": "https://learn.lovelace.academy/tokens/nft-minting-guide/",
"image": "ipfs://$IPFS_CID"
}
}
}
}
📝 Version 1.0 of the NFT Metadata standard defines the asset_name to be a text instead of hexadecimal representation i.e. “LALOGO” instead of “4c414c4f474f”
Get the Latest Protocol Parameters
The current set of Cardano protocol parameters are required to calculate Tx fees and we can retrieve them into the file protocol.json with the following command.
cardano-cli query protocol-parameters --testnet-magic 1097911063 --out-file protocol.json
Build draft Tx to Calculate Fee
In this example we are minting one token under our NFT-specific policy with the asset name LALOGO and attaching the NFT standard metadata file. The cardano-cli transaction build-raw command as of v1.32.0 only accepts hexadecimal encoded asset names so we also have to derive shell variable $NFT_ASSETHEX.
NFT_ASSETNAME=LALOGO
NFT_ASSETHEX=$(echo -n $NFT_ASSETNAME | xxd -b -ps -c 80 | tr -d '\n')
MIN_LOVELACE=1880000
TXOUT_CHANGE=$(expr $UTXO0V - $MIN_LOVELACE)
cardano-cli transaction build-raw \
--tx-in $UTXO0H#$UTXO0I \
--tx-out $DESTADDR+$MIN_LOVELACE+"1 $POLICYID.$NFT_ASSETHEX" \
--tx-out $SOURCEADDR+$TXOUT_CHANGE \
--metadata-json-file nft-metadata.json \
--mint "1 $POLICYID.$NFT_ASSETHEX" \
--minting-script-file nft-policy.script \
--invalid-hereafter $EXPIRES_AT_SLOT \
--fee 0 \
--out-file fee_draft.txraw
FEE=$(cardano-cli transaction calculate-min-fee --tx-body-file fee_draft.txraw --tx-in-count 1 --tx-out-count 2 --witness-count 2 --testnet-magic 1097911063 --protocol-params-file protocol.json | egrep -o '[0-9]+')
Following a similar approach in Transactions: UTxO and Metadata
, we build a draft Tx with the same arguments to calculate the Tx fee captured in the FEE shell variable. This time we are specifying additional arguments in the form of --mint, --minting-script-file and --invalid-hereafter. Also note the --witness-count of 2 when we calculate the fee which indicates that we need to sign it with both the source payment signing key and the NFT minting policy key.
As with minting fungible tokens, the most difficult part is building the raw Tx with the correct --tx-out and --mint parameters. The format for --tx-out is {address}+{lovelace_quantity}+1 {policyid}.{asset_name} for NFTs to ensure a quantity of 1 with additional NFTs optionally concatenated with a quantity of 1 and a different asset_name. The format for --mint is the same as --tx-out without the {address}+{lovelace_quantity} in the beginning.
📝🔥 Burn NFTs by using a quantity of -1, e.g. --mint -1 629718e24d22e0c02c2efd27290e1a58ebc2972635a7c523aee2d8fc.4c414c4f474f
Build Raw Minting Tx
Now we can build out the actual Tx with the correct fee and using that to calculate the TXOUT_CHANGE to go back to the source address. As described in the previous article Cardano’s Native Assets
we also need to specify a minimum amount of lovelace to send with the custom tokens to the destination address.
MIN_LOVELACE=1880000
TXOUT_CHANGE=$(expr $UTXO0V - $FEE - $MIN_LOVELACE)
cardano-cli transaction build-raw \
--tx-in $UTXO0H#$UTXO0I \
--tx-out $DESTADDR+$MIN_LOVELACE+"1 $POLICYID.$NFT_ASSETHEX" \
--tx-out $SOURCEADDR+$TXOUT_CHANGE \
--metadata-json-file nft-metadata.json \
--mint "1 $POLICYID.$NFT_ASSETHEX" \
--minting-script-file nft-policy.script \
--invalid-hereafter $EXPIRES_AT_SLOT \
--fee $FEE \
--out-file mint.txraw
Sign Raw Minting Tx
Note that we are signing the Tx with both nft-policy.skey and source.skey to provide two witnesses to the Tx.
cardano-cli transaction sign \
--signing-key-file nft-policy.skey \
--signing-key-file source.skey \
--testnet-magic 1097911063 \
--tx-body-file mint.txraw \
--out-file mint.txsigned
Submit Signed Tx
cardano-cli transaction submit --tx-file mint.txsigned --testnet-magic 1097911063
Get Transaction ID
You can also get the transaction ID (aka Tx Hash) of your Tx with the command:
cardano-cli transaction txid --tx-file mint.txsigned
This can be used to verify the result in a testnet block explorer like Cardanoscan or ADATools through a direct search of the transaction ID above. For example the output of this example can be seen here.
Burning Tokens
To burn NFTs you will need to specify a negative value of 1 (i.e. -1) following your {policyid}.{assetname} unit in the --mint parameter, use the same --minting-script-file and ensure the --tx-out values remove the +1 {policyid}.{assetname} segment.
Explore Token Builders
Alternatively you can use the following tools tools to mint your own tokens without having to use the CLI commands against a full node.
References
Start Integrating with Cardano
Had enough of the cardano-cli and want to start integrating with Cardano using a familiar tech stack? Continue to Integrating Cardano: Summary of Components ➡️


